Seliciclib
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
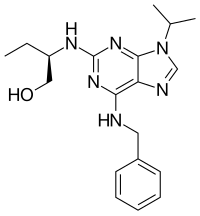
2-(R)-(1-Ethyl-2-hydroxyethylamino)-6-benzylamino-9-isopropylpurine
|
|
| Other names
Roscovitine; CYC202
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | roscovitine |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C19H26N6O | |
| Molar mass | 354.46 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Seliciclib (roscovitine or CYC202) is an experimental drug candidate in the family of pharmacological cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors that preferentially inhibit multiple enzyme targets including CDK2, CDK7 and CDK9, which alter the growth phase or state within the cell cycle of treated cells. Seliciclib is being developed by Cyclacel.
Seliciclib is being researched for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), Cushing's disease, leukemia, HIV infection, herpes simplex infection, cystic fibrosis and the mechanisms of chronic inflammation disorders.
Seliciclib is a 2,6,9-substituted purine analog. Its structure in complex with CDK2 was determined in 1996. Seliciclib inhibits CDK2/E, CDK2/A, CDK7 and CDK9.
Seliciclib has been found to produce apoptosis in treated cancerous cells of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other cancers. Seliciclib has previously undergone Phase IIa clinical trials, in 240 NSCLC patients as a combined dose with existing first- and second-line treatments. In the current APPRAISE trial, the research drug is undergoing Phase IIb clinical trial as a monotherapy for NSCLC in third-line patients. The side-effects reported in Phase I trials of seliciclib for NSCLC were "nausea, vomiting, transient elevations in serum creatinine and liver function parameters and transient hypokalemia".
...
Wikipedia
