Scarabs
| Scarab beetle | |
|---|---|
 |
|
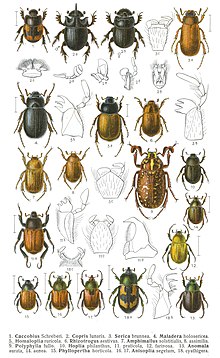
| Central European scarab beetles with some anatomical details. Edmund Reitter's Fauna Germanica, 1908 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Coleoptera |
| Superfamily: | Scarabaeoidea |
| Family: |
Scarabaeidae Latreille, 1802 |
| Subfamilies | |
|
Aegialiinae |
|
Aegialiinae
Allidiostomatinae
Aphodiinae
Cetoniinae
Dynastinae
Dynamopodinae
Euchirinae
Melolonthinae
Orphninae
Pachypodinae
Phaenomeridinae
Phileurinae
Rutelinae
Scarabaeinae
Termitotroginae
The family Scarabaeidae as currently defined consists of over 30,000 species of beetles worldwide, often called scarabs or scarab beetles. The classification of this family is fairly unstable, with numerous competing theories, and new proposals appearing quite often. Many of the subfamilies listed here probably will not be recognized very much longer, as they will likely be reduced in status below subfamily rank, or elevated to family status (the latter is most likely, e.g., with the family "Melolonthidae" already appearing in some recent classifications). Other families have been removed recently, and are nearly universally accepted (e.g., Pleocomidae, Glaresidae, Glaphyridae, Ochodaeidae, Geotrupidae, and Bolboceratidae).
Scarabs are stout-bodied beetles, many with bright metallic colours, measuring between 1.5 and 160 mm. They have distinctive, clubbed antennae composed of plates called lamellae that can be compressed into a ball or fanned out like leaves to sense odours. The front legs of many species are broad and adapted for digging.
The C-shaped larvae, called grubs, are pale yellow or white. Most adult beetles are nocturnal, although the flower chafers (Cetoniinae) and many leaf chafers (Rutelinae) are active during the day. The grubs mostly live underground or under debris, so are not exposed to sunlight. Many scarabs are scavengers that recycle dung, carrion, or decaying plant material. Others, such as the Japanese beetle, are devastating agricultural pests.
...
Wikipedia
