Saphenous nerve
| Saphenous nerve | |
|---|---|
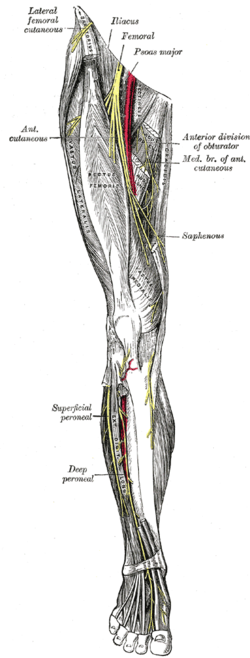
Nerves of the right lower extremity. Front view. (Saphenous labeled at center right.)
|
|
| Details | |
| From | femoral nerve (L3, L4) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus saphenus |
| TA | A14.2.07.023 |
| FMA | 45262 |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
The saphenous nerve (long or internal saphenous nerve) is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve. It is a strictly sensory nerve, and has no motor function.
It approaches the femoral artery where this vessel passes beneath the sartorius, and lies in front of the artery, behind the aponeurotic covering of the adductor canal, as far as the opening in the lower part of the Adductor magnus.
Here it diverges from the artery, and emerges from behind the lower edge of the aponeurotic covering of the canal; it descends vertically along the medial side of the knee behind the sartorius, pierces the fascia lata, between the tendons of the Sartorius and Gracilis, and becomes subcutaneous.
The nerve then passes along the tibial side of the leg, accompanied by the great saphenous vein, descends behind the medial border of the tibia, and, at the lower third of the leg, divides into two branches:
The saphenous nerve, about the middle of the thigh, gives off a branch which joins the subsartorial plexus.
At the medial side of the knee it gives off a large infrapatellar branch, which pierces the sartorius and fascia lata, and is distributed to the skin in front of the patella.
Below the knee, the branches of the saphenous nerve (medial crural cutaneous branches) are distributed to the skin of the front and medial side of the leg, communicating with the cutaneous branches of the femoral, or with filaments from the obturator nerve.
...
Wikipedia
