Romanic
| Romance | |
|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Latin peoples |
| Geographic distribution |
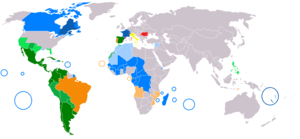
Originated in coastal Mediterranean and western Europe; now also spoken all over the Americas, much of Africa and in parts of Southeast Asia and Oceania |
| Linguistic classification |
Indo-European
|
|
Early form
|
|
| Subdivisions | |
| ISO 639-5 | |
| Linguasphere | 51- (phylozone) |
| Glottolog | roma1334 |
 |
|
 |
|
The Romance languages (sometimes called the Romanic languages, Latin languages, or Neo-Latin languages) are the modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin between the sixth and ninth centuries and that thus form a branch of the Italic languages within the Indo-European language family.
Today, around 800 million people are native speakers worldwide, mainly in Europe, Africa and the Americas, but also elsewhere. Additionally, the major Romance languages have many non-native speakers and are in widespread use as lingua francas. This is especially the case for French, which is in widespread use throughout Central and West Africa, Madagascar, Mauritius and the Maghreb.
The five most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are Spanish (410 million), Portuguese (250 million), French (80 million), Italian (60 million), and Romanian (25 million).
Because of the difficulty of imposing boundaries on a continuum, various counts of the modern Romance languages are given; for example, Dalby lists 23 based on mutual intelligibility. The following, more extensive list, includes 35 current, living languages, and one recently extinct language, Dalmatian:
It should be noted that any count of the number of Romance languages should be taken as an approximation entirely dependent upon the criteria adopted for selection. Lists such as the one above are accurately interpreted as typologies, i.e. under any single label is a collection of varieties that share many features but are sufficiently distinct in detail to be considered separate languages unto themselves. By way of example, in the collection under Ligurian, an item as basic as 'mirror' can vary as much as Eastern Ligurian [ˈspeʧo], Central Ligurian [ˈspedːʒu], Western Ligurian [ˈspeʎu], while 'flour' is ['fɛŋa], [fa'iŋa], ['fajna], ['faɹina], ['faɹina], [fa'ina] or [fa'rejŋna], depending upon the locale. Similar differences can be present in syntax and morphology.[3]
...
Wikipedia
