Robinow syndrome
| Robinow syndrome | |
|---|---|
 |
|
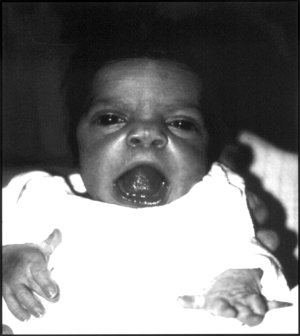
| An infant exhibiting the facial features of Robinow syndrome. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q87.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 759.8 |
| OMIM | 180700 |
Robinow syndrome is an extremely rare genetic disorder characterized by short-limbed dwarfism, abnormalities in the head, face, and external genitalia, as well as vertebral segmentation. The disorder was first described in 1969 by human geneticist Meinhard Robinow, along with physicians Frederic N. Silverman and Hugo D. Smith, in the American Journal of Diseases of Children. By 2002, over 100 cases had been documented and introduced into medical literature.
Two forms of the disorder exist, dominant and recessive, of which the former is more common. Patients with the dominant version often suffer moderately from the aforementioned symptoms. Recessive cases, on the other hand, are usually more physically marked, and individuals may exhibit more skeletal abnormalities. The recessive form is particularly frequent in Turkey. However, this can likely be explained by a common ancestor, as these patients' families can be traced to a single town in Eastern Turkey. Clusters of the autosomal recessive form have also been documented in Oman and Czechoslovakia.
The syndrome is also known as Robinow-Silverman-Smith syndrome, Robinow dwarfism, fetal face, fetal face syndrome, fetal facies syndrome, acral dysostosis with facial and genital abnormalities, or mesomelic dwarfism-small genitalia syndrome. The recessive form was previously known as Covesdem syndrome.
Robinow noted the resemblance of affected patients' faces to that of a fetus, using the term "fetal facies" to describe the appearance of a small face and widely spaced eyes. Clinical features also may include a short, upturned nose, a prominent forehead, and a flat nasal bridge. The upper lip may be "tented", exposing dental crowding, "tongue tie", or gum hypertrophy.
...
Wikipedia
