Rifapentine
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a602026 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | increases when administered with food |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | 3{[(4-cyclopentyl-1-piperazinyl)imino]methyl}rifamycin |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.057.021 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
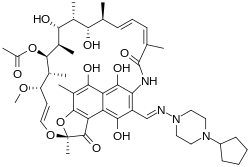
| Formula | C47H64N4O12 |
| Molar mass | 877.031 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Rifapentine (RPT), sold under the brand name Priftin, is an antibiotic used in the treatment of tuberculosis. In active tuberculosis it is used together with other antituberculosis medications. In latent tuberculosis it is typically used with isoniazid. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include low neutrophil counts in the blood, elevated liver enzymes, and white blood cells in the urine. Serious side effects may include liver problems or Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea. It is unclear if use during pregnancy is safe. Rifapentine is in the rifamycin family of medication and works by blocking DNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
Rifapentine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1988. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. In the United States it costs 100 to 200 USD per month. In many areas of the world it is not easy to get as of 2015.
A review of alternative regimens for prevention of active tuberculosis in HIV-negative individuals with latent TB found that a weekly, directly observed regimen of rifapentine with isoniazid for three months was as effective as a daily, self -administered regimen of isoniazid for nine months. But the rifapentine-isoniazid regimen had higher rates of treatment completion and lower rates of hepatotoxicity. However, the rate of treatment-limiting adverse events was higher in the rifapentine-isoniazid regimen.
Rifapentine has been assigned a Pregnancy Category C by the FDA. Rifapentine in pregnant women has not been studied, but animal reproduction studies have resulted in fetal harm and were teratogenic. If rifapentine and rifampin are used together in pregnancy, coagulation should be monitored due to a possible increased risk of maternal postpartum hemorrhage and infant bleeding.
...
Wikipedia
