Retropharyngeal abscess
| Retropharyngeal abscess | |
|---|---|
 |
|
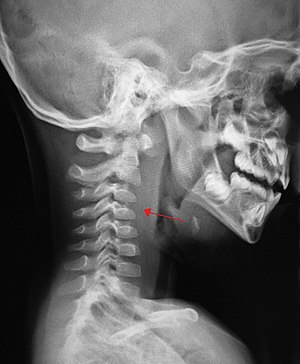
| A lateral cervical spine x-ray demonstrating prevertebral soft tissue swelling (marked by the arrow) as seen in a person with a retropharyngeal abscess. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | pulmonology |
| ICD-10 | J39.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 478.24 |
| DiseasesDB | 11461 |
| MedlinePlus | 000984 |
| eMedicine | emerg/506 ped/2682 |
| MeSH | D017703 |
Retropharyngeal abscess (RPA) is an abscess located in the tissues in the back of the throat behind the posterior pharyngeal wall (the retropharyngeal space). Because RPAs typically occur in deep tissue, they are difficult to diagnose by physical examination alone. RPA is a relatively uncommon illness, and therefore may not receive early diagnosis in children presenting with stiff neck, malaise, difficulty swallowing, or other symptoms listed below. Early diagnosis is key, while a delay in diagnosis and treatment may lead to death. Parapharyngeal space communicates with retropharyngeal space and an infection of retropharyngeal space can pass down behind the esophagus into the mediastinum. RPAs can also occur in adults of any age.
RPA can lead to airway obstruction or sepsis – both life-threatening emergencies. Fatalities normally occur from patients not receiving treatment immediately and suffocating prior to knowing that anything serious was wrong.
Signs and symptoms may include stiff neck (limited neck mobility or torticollis), some form of palpable neck pain (may be in "front of the neck" or around the Adam's Apple), malaise, difficulty swallowing, fever, stridor, drooling, croup-like cough or enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Any combination of these symptoms should arouse suspicion of RPA.
RPA is usually caused by a bacterial infection originating from the nasopharynx, tonsils, sinuses, adenoids or middle ear. Any upper respiratory infection (URI) can be a cause. RPA can also result from a direct infection due to penetrating injury or a foreign body. RPA can also be linked to young children who do not have adequate dental care or brush their teeth properly.
...
Wikipedia
