Rete mirabile
| Rete mirabile | |
|---|---|
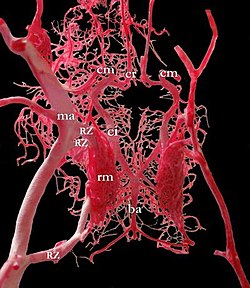
Rete mirabile of a sheep
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| TA | A12.0.00.013 |
| FMA | 76728 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
A rete mirabile (Latin for "wonderful net"; plural retia mirabilia) is a complex of arteries and veins lying very close to each other, found in some vertebrates, mainly warm-blooded ones. The rete mirabile utilizes countercurrent blood flow within the net (blood flowing in opposite directions) to act as a countercurrent exchanger. It exchanges heat, ions, or gases between vessel walls so that the two bloodstreams within the rete maintain a gradient with respect to temperature, or concentration of gases or solutes. This term was coined by Galen.
The effectiveness of retia is primarily determined by how readily the heat, ions, or gases can be exchanged. For a given length, they are most effective with respect to gases or heat, then small ions, and decreasingly so with respect to other substances.
The retia can provide for extremely efficient exchanges. In bluefin tuna, for example, nearly all of the metabolic heat in the venous blood is transferred to the arterial blood, thus conserving muscle temperature; that heat exchange approaches 99% efficiency.
In birds with webbed feet, retia mirabilia in the legs and feet transfer heat from the outgoing (hot) blood in the arteries to the incoming (cold) blood in the veins. The effect of this biological heat exchanger is that the internal temperature of the feet is much closer to the ambient temperature, thus reducing heat loss. Penguins have them also in the flippers and nasal passages.
Seabirds distill seawater using countercurrent exchange in a gland with a rete mirabile. The gland secretes highly concentrated brine stored near the nostrils above the beak. The bird then "sneezes" the brine out. As freshwater is not usually available in their environments, some seabirds, such as pelicans, petrels, albatrosses, gulls and terns, possess this gland, which allows them to drink the salty water from their environments while they are hundreds of miles away from land.
...
Wikipedia
