Respiratory epithelium
| Respiratory epithelium | |
|---|---|
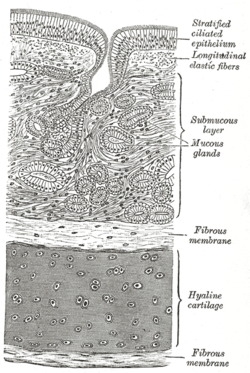
Diagram of the trachea showing respiratory epithelium at the top
|
|
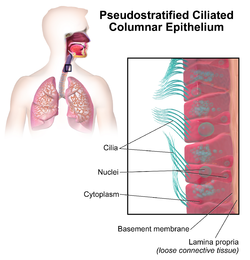
Illustration depicting Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium.
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| Code | TH H3.05.00.0.00003 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
Respiratory epithelium is a type of epithelium found lining the respiratory tract, where it serves to moisten and protect the airways. It also functions as a barrier to potential pathogens and foreign particles, preventing infection and tissue injury by the action of mucociliary clearance.
The respiratory epithelium lining the upper respiratory airways is classified as ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. This designation is due to the arrangement of the multiple cell types composing the respiratory epithelium. While all cells make contact with the basement membrane and are, therefore, a single layer of cells, the nuclei are not aligned in the same plane. Hence, it appears as though several layers of cells are present and the epithelium is called pseudostratified.
The majority of cells composing the ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium are of three types: a) ciliated cells, b) goblet cells, and c) basal cells. The ciliated cells are columnar epithelial cells with specialized ciliary modifications. Goblet cells, so named because they are shaped like a wine goblet, are columnar epithelial cells that contain membrane-bound mucous granules and secrete mucus, or epithelial lining fluid (ELF), the composition of which is tightly regulated; the mucus helps maintain epithelial moisture and traps particulate material and pathogens moving through the airway. and determines how well mucociliary clearance works. The basal cells are small, nearly cuboidal cells thought to have some ability to differentiate into other cells types found within the epithelium. For example, these basal cells respond to injury of the airway epithelium, migrating to cover a site denuded of differentiated epithelial cells, and subsequently differentiating to restore a healthy epithelial cell layer.
...
Wikipedia
