Red Fox
| Red fox Temporal range: 0.7–0 Ma Middle –present |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
|
European red fox (V. v. crucigera) photographed at the British Wildlife Centre in Surrey, England.
|
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Caniformia |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | Vulpes |
| Species: | V. vulpes |
| Binomial name | |
|
Vulpes vulpes (Linnaeus, 1758) |
|
| Subspecies | |
 |
|
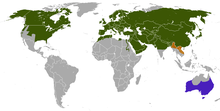
| Distribution of the red fox
native
introduced presence uncertain |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Canis vulpes
(Linnaeus, 1758) |
|
The red fox (Vulpes vulpes), largest of the true foxes, has the greatest geographic range of all members of the Carnivora family, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere from the Arctic Circle to North Africa, North America and Eurasia. It is listed as least concern by the IUCN. Its range has increased alongside human expansion, having been introduced to Australia, where it is considered harmful to native mammals and bird populations. Due to its presence in Australia, it is included among the list of the "world's 100 worst invasive species".
The red fox originated from smaller-sized ancestors from Eurasia during the Middle Villafranchian period, and colonised North America shortly after the Wisconsin glaciation. Among the true foxes, the red fox represents a more progressive form in the direction of carnivory. Apart from its large size, the red fox is distinguished from other fox species by its ability to adapt quickly to new environments. Despite its name, the species often produces individuals with other colourings, including albinos and melanists. Forty-five subspecies are currently recognised, which are divided into two categories: the large northern foxes, and the small, basal southern foxes of Asia and North Africa.
Red foxes are usually together in pairs or small groups consisting of families, such as a mated pair and their young, or a male with several females having kinship ties. The young of the mated pair remain with their parents to assist in caring for new kits. The species primarily feeds on small rodents, though it may also target rabbits, game birds, reptiles, invertebrates and young ungulates. Fruit and vegetable matter is also eaten sometimes. Although the red fox tends to kill smaller predators, including other fox species, it is vulnerable to attack from larger predators, such as wolves, coyotes, golden jackals and medium- and large-sized felines.
...
Wikipedia

