Quercitin
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
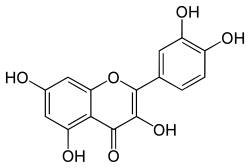
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one
|
|
| Other names
Sophoretin
Meletin Quercetine Xanthaurine Quercetol Quercitin Quertine Flavin meletin |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.807 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C15H10O7 | |
| Molar mass | 302.236 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.799 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 316 °C (601 °F; 589 K) |
| Practically insoluble in water; soluble in aqueous alkaline solutions | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Quercetin /ˈkwɜːrsᵻtᵻn/ is a flavonol found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, and grains. It can be used as an ingredient in supplements, beverages, or foods.
While quercetin supplements have been promoted for prevention and treatment of cancer, "there is no reliable clinical evidence that quercetin can prevent or treat cancer in humans". Also, there is no evidence that consuming foods rich in quercetin reduces the risk of cancer or any other disease.
Quercetin supplements have also been promoted for the treatment of a wide spectrum of other diseases. However, the European Food Safety Authority evaluated possible health claims associated with consumption of quercetin, and found that no cause-and-effect relationship has been established for any physiological effect in human health or diseases.
Quercetin is contraindicated with some antibiotics; it may interact with fluoroquinolones (a class of antibiotics), as quercetin competitively binds to bacterial DNA gyrase. Whether this inhibits or enhances the effect of fluoroquinolones is not certain.
As paclitaxel is metabolized primarily by CYP2C8, its bioavailability may be increased unpredictably by quercetin, potentially leading to harmful side effects.
Quercetin is a flavonoid widely distributed in nature. The name has been used since 1857, and is derived from quercetum (oak forest), after Quercus. It is a naturally occurring polar auxin transport inhibitor.
...
Wikipedia
