Pulmonary veins
| Pulmonary Veins | |
|---|---|

Diagram of the alveoli with both cross-section and external view.
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | truncus arteriosus |
| Drains from | lungs |
| Drains to | left atrium |
| Artery | pulmonary artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | venae pulmonales |
| MeSH | A07.231.908.713 |
| TA | A12.3.02.001 |
| FMA | 70827 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
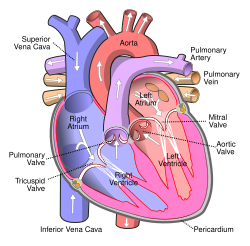
The pulmonary veins are large blood vessels that receive oxygenated blood from the lungs and drain into the left atrium of the heart. There are four pulmonary veins, two from each lung. The pulmonary veins are among the few veins that carry oxygenated blood.
Two pulmonary veins emerge from each lung hilum, receiving blood from three or four bronchial veins apiece and draining into the left atrium. An inferior and superior vein drains each lung, so there are four veins in total. The veins are fixed to the pericardium. The pulmonary veins travel alongside the pulmonary arteries
At the root of the lung, the right superior pulmonary vein lies in front of and a little below the pulmonary artery; the inferior is situated at the lowest part of the lung hilum. Behind the pulmonary artery is the bronchus.
The right pulmonary veins (contains oxygenated blood) pass behind the right atrium and superior vena cava; the left in front of the descending thoracic aorta.
Occasionally the three veins on the right side remain separate, and not infrequently the two left pulmonary veins end by a common opening into the left atrium. Therefore, the number of pulmonary veins opening into the left atrium can vary between three and five in the healthy population.
The two left pulmonary veins may be united as a single pulmonary vein in about 25% of people; the two right veins may be united in about 3%.
The pulmonary veins play an essential role in respiration, by receiving blood that has been oxygenated in the alveoli and returning it to the left atrium.
As part of the pulmonary circulation they carry oxygenated blood back to the heart, as opposed to the veins of the systemic circulation which carry deoxygenated blood.
...
Wikipedia