Prunus pensylvanica
| Prunus pensylvanica | |
|---|---|
 |
|
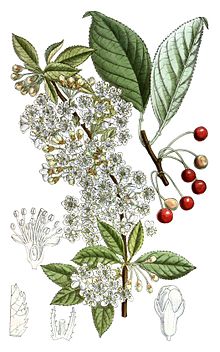
| 1913 illustration | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Rosaceae |
| Genus: | Prunus |
| Subgenus: | Cerasus |
| Species: | P. pensylvanica |
| Binomial name | |
|
Prunus pensylvanica L.f. 1782 |
|
 |
|
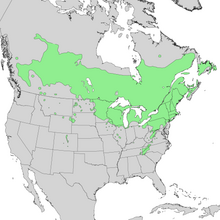
| Natural range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Prunus pensylvanica, also known as bird cherry,fire cherry,pin cherry, and red cherry, is a North American cherry species in the genus Prunus.
Prunus pensylvanica, grows as a shrub or small tree, usually with a straight trunk and a narrow, round-topped crown. It grows 5–15 m (16–49 ft) tall and 10–51 cm (3.9–20.1 in) in diameter. Trees up to 30 m (98 ft) tall have been found growing in the southern Appalachians, with the largest found on the western slopes of the Great Smoky Mountains. Its foliage is thin, with leaves 4–11 cm (1.6–4.3 in) long and 1–4.5 cm (0.39–1.77 in) wide. Flowers occur in small groupings of five to seven with individual flowers 1 cm (0.39 in) across. The fruit are drupes, ranging from 4–8 mm (0.16–0.31 in), each with a single seed 4–6 mm (0.16–0.24 in) in diameter contained within a hard "stone".
Prunus pensylvanica is widespread across much of Canada from Newfoundland and southern Labrador to British Columbia and the southern Northwest Territories. Additionally it is very common in New England and the Great Lakes region. It can also be found in the Appalachian Mountains as far south as northern Georgia and eastern Tennessee. Scattered growth of the Pin cherry also occurs in the Rocky Mountains, south to Colorado as well as in the Black Hills of South Dakota.
The pin cherry can regenerate by seed and sprout. Its flowers are bisexual and pollinated by insects. Seeds are dispersed by birds, small mammals, and gravity. As part of its reproductive strategy, pin cherries seeds can remain viable in the soil for many years. Seeds accumulate over prolonged periods, and soil seed banks may be viable for 50–100 years. Asexual reproduction is achieved by sprouting, and often thickets of pin cherry plants form.
...
Wikipedia
