Protein A
| Protein A | |
|---|---|
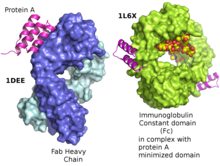
Structure of a domain of protein A as a three-helix bundle binding to the heavy variable chain of a VH3 human Fab left. Minimized protein A bound to Fc fragment of Rituximab.
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SpA |
| SCOP | 1DEE |
| SUPERFAMILY | 1DEE |
Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. It has found use in biochemical research because of its ability to bind immunoglobulins. It is composed of five homologous Ig-binding domains that fold into a three-helix bundle. Each domain is able to bind proteins from many mammalian species, most notably IgGs. It binds the heavy chain within the Fc region of most immunoglobulins and also within the Fab region in the case of the human VH3 family. Through these interactions in serum, where IgG molecules are bound in the wrong orientation (in relation to normal antibody function), the bacteria disrupts opsonization and phagocytosis.
As a by-product of his work on type-specific staphylococcus antigens, Verwey reported 1940 that a protein fraction prepared from extracts of these bacteria non-specifically precipitated rabbit antisera raised against different staphylococcus types. In 1958, Jensen confirmed Verwey’s finding and showed that rabbit pre-immunization sera as well as normal human sera bound to the active component in the staphylococcus extract; he designated this component Antigen A (because it was found in fraction A of the extract) but thought it was a polysaccharide. The misclassification of the protein was the result of faulty tests but it was not long thereafter (1962) that Löfkvist and Sjöquist corrected the error and confirmed that Antigen A was in fact a surface protein on the bacterial wall of certain strains of S. aureus. The Bergen group from Norway named the protein "Protein A" after the antigen fraction isolated by Jensen.
It has been shown via crystallographic refinement that the primary binding site for protein A is on the Fc region, between the CH2 and CH3 domains. In addition, protein A has been shown to bind human IgG molecules containing IgG F(ab')2 fragments from the human VH3 gene family.
...
Wikipedia
