Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
| High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia | |
|---|---|
 |
|
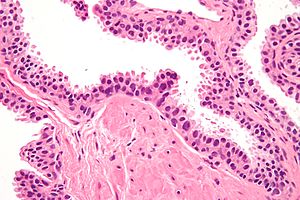
| Micrograph showing high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. H&E stain. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-9-CM | 233.4 |
In urologic pathology, high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, abbreviated HGPIN, is an abnormality of prostatic glands and believed to precede the development of prostate adenocarcinoma (the most common form of prostate cancer).
It may be referred to simply as prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (abbreviated as PIN). It is considered to be a pre-malignancy, or carcinoma in situ, of the prostatic glands.
HGPIN in isolation is asymptomatic. It is typically discovered in prostate biopsies taken to rule-out prostate cancer and very frequently seen in prostates removed for prostate cancer.
On a subsequent biopsy, given a history of a HGPIN diagnosis, the chance of finding prostatic adenocarcinoma is approximately 30%.
HGPIN is diagnosed from tissue by a pathologist, which may come from:
Blood tests for prostate specific antigen (PSA), digital rectal examination, ultrasound scanning of the prostate via the rectum, fine needle aspiration or medical imaging studies (such as magnetic resonance imaging) are not useful for diagnosing HGPIN.
HGPIN typically has one of four different histologic patterns:
Its cytologic features are that of prostatic adenocarcinoma:
...
Wikipedia
