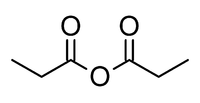
Propionic anhydride
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Propanoic anhydride
|
|
| Other names
Propionic anhydride
Propanoyl propanoate |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.218 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | UF9100000 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 130.14 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear liquid, with a strong smell similar to vinegar |
| Density | 1.015 g/cm3, liquid |
| Melting point | −42 °C (−44 °F; 231 K) |
| Boiling point | 167 to 170 °C (333 to 338 °F; 440 to 443 K) |
| Reacts to give propanoic acid | |
| Viscosity | 1.144 cP at ?°C |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | flammable |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| R-phrases | R34 |
| S-phrases | S26-45 |
| Flash point | 63 °C (145 °F; 336 K) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Acetic anhydride |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Propanoic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula (CH3CH2CO)2O. This simple acid anhydride is a colourless liquid. It is a widely used reagent in organic synthesis.
Propanoic anhydride has been prepared by dehydration of propanoic acid using ketene:
Propanoic anhydride is strong smelling and corrosive, and will cause burns on contact with skin. Vapour can burn eyes and lungs.
Due to its potential use as a precursor in the synthesis of fentanyl and fentanyl analogs, propanoic anhydride is regulated by the United States Drug Enforcement Administration as a List I chemical under the Controlled Substances Act.
...
Wikipedia
