Posterior compartment of thigh
| Posterior compartment of thigh | |
|---|---|

Cross-section through the middle of the thigh. (Posterior compartment is at center bottom.)
|
|
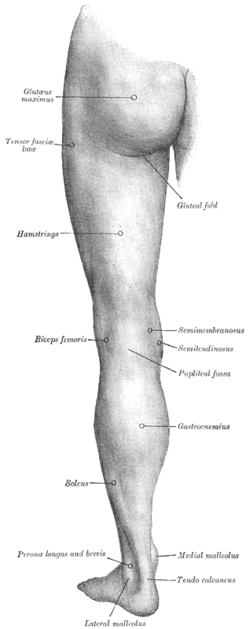
Back of left lower extremity.
|
|
| Details | |
| Artery | inferior gluteal artery, profunda femoris artery, perforating arteries |
| Nerve | sciatic nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | compartimentum femoris posterius |
| TA | A04.7.01.003 |
| FMA | 45157 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The posterior compartment of the thigh is one of the fascial compartments that contains the knee flexors and hip extensors known as the hamstring muscles, as well as vascular and nervous elements, particularly the sciatic nerve.
The posterior compartment is a fascial compartment bounded by fascia. It is separated from the anterior compartment by two folds of deep fascia, known as the medial intermuscular septum and the lateral intermuscular septum.
The muscles of the posterior compartment of the thigh are the:
These muscles (or their tendons) apart from the short head of the biceps femoris, are commonly known as the hamstrings. The depression at the back of the knee, or kneepit is the popliteal fossa, colloquially called the ham. The tendons of the above muscles can be felt as prominent cords on both sides of the fossa—the biceps femoris tendon on the lateral side and the semimembranosus and semitendinosus tendons on the medial side. The hamstrings flex the knee, and aided by the gluteus maximus, they extend the hip during walking and running. The semitendinosus is named for its unusually long tendon. The semimembranosus is named for the flat shape of its superior attachment.
The hamstrings are innervated by the sciatic nerve, specifically by a main branch of it: the tibial nerve. (The short head of the biceps femoris is innervated by the common fibular nerve). The sciatic nerve runs along the longitudinal axis of the compartment, giving the cited terminal branches close to the superior angle of the popliteal fossa.
...
Wikipedia
