Planum Boreum
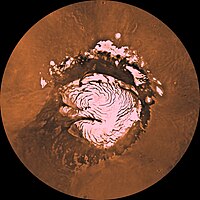
Viking mosaic of Planum Boreum and surrounds
|
|
| Coordinates | 88°00′N 15°00′E / 88.0°N 15.0°ECoordinates: 88°00′N 15°00′E / 88.0°N 15.0°E |
|---|---|
Planum Boreum (Latin: "the northern plain") is the northern polar plain on Mars. It extends northward from roughly 80°N and is centered at 88°00′N 15°00′E / 88.0°N 15.0°E. Surrounding the high polar plain is a flat and featureless lowland plain called Vastitas Borealis which extends for approximately 1500 kilometres southwards, dominating the northern hemisphere.
The main feature of the Planum Boreum is a large fissure or canyon in the polar ice cap called Chasma Boreale. It is up to 100 kilometres (62 mi) wide and features scarps up to 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) high. By comparison, the Grand Canyon is approximately 1.6 kilometres (0.99 mi) deep in some places and 446 kilometres (277 mi) long but only up to 24 kilometres (15 mi) wide. Chasma Boreale cuts through polar deposits and ice, such as those present at Greenland.
Planum Boreum interfaces with Vastitas Borealis west of Chasma Boreale at an irregular scarp named Rupes Tenuis. This scarp reaches heights of up to 1 km. At other places, the interface is a collection of mesas and troughs.
Planum Boreum is surrounded by large fields of sand dunes spanning from 75°N to 85°N. These dune fields are named Olympia Undae, Abalos Undae and Hyperboreae Undae. Olympia Undae, by far the largest, covers from 100°E to 240°E. Abalos Undae covers from 261°E to 280°E and Hyperboreale Undae spans from 311°E to 341°E. See also List of extraterrestrial dune fields.
Planum Boreum is home to a permanent ice cap consisting mainly of water ice (with a 1 m thick veneer of carbon dioxide ice during the winter). It has a volume of 1.2 million cubic kilometres and covers an area equivalent to about 1.5 times the size of Texas. It has a radius of 600 km. The maximum depth of the cap is 3 km.
...
Wikipedia
