Pinus torreyana
|
Pinus torreyana Torrey pine |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| A Torrey pine on the northeast coast of Santa Rosa Island, California | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Pinaceae |
| Genus: | Pinus |
| Subgenus: | Pinus |
| Species: | P. torreyana |
| Binomial name | |
|
Pinus torreyana Parry ex Carr. |
|
 |
|
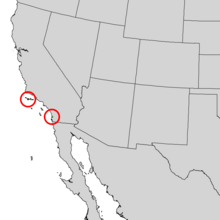
| Natural range of Pinus torreyana | |
The Torrey pine, Pinus torreyana, is a rare pine species in the United States. It is an endangered species growing only in the Torrey Pines State Natural Reserve, coastal northern San Diego county, and on one of the Channel Islands. This species is endemic to the coastal sage and chaparral ecoregion in the U.S. state of California.
Pinus torreyana is a broad, open-crowned pine tree growing to 8–17 meters (26–56 ft) tall in the wild, with 25–30 centimeters (9.8–11.8 in) long leaves ('needles') in groups of five. The cones are stout and heavy, typically 8–15 cm (3.1–5.9 in) long and broad, and contain large, hard-shelled, but edible, pine nuts. The species name torreyana is named for John Torrey, an American botanist, after whom the coniferous genus Torreya is also named.
The "wild" native population of Pinus torreyana is restricted to trees growing in a narrow strip along the Southern California coast in San Diego. There is also a population of the variety Pinus torreyana var. insularis in two groves on Santa Rosa Island, a California Channel Island off the coast of Santa Barbara. The presence of Torrey pines along the semi-arid coast of San Diego and Santa Rosa Island (rainfall less than 15 inches per year) is probably a relic population of a much more extensive Ice Age distribution. Coastal fog during spring and summer along the San Diego and Santa Rosa Island coast provides just enough moisture to supplement the fairly low winter rainfall, allowing for survival of the species in the wild habitat zone.
...
Wikipedia

