Phospholamban
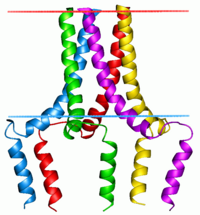
Phospholamban pentamer
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Phospholamban | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF04272 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR005984 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1fjk | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1fjk | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.A.50 | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 70 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1zll | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
n/a
Phospholamban, also known as PLN or PLB, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PLN gene. Phospholamban is a 52-amino acid integral membrane protein that regulates the Ca2+ pump in cardiac muscle cells.
This protein is found as a pentamer and is a major substrate for the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) in cardiac muscle. The protein is an inhibitor of cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca++-ATPase (SERCA2) in the unphosphorylated state, but inhibition is relieved upon phosphorylation of the protein. The relief of inhibition on Ca++-ATPase leads to faster Ca++ uptake into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, thereby contributing to the lusitropic response elicited in heart by beta-agonists. The protein is a key regulator of cardiac diastolic function . Mutations in this gene are a cause of inherited human dilated cardiomyopathy with refractory congestive heart failure.
...
Wikipedia