Phenylalanine—tRNA ligase
| phenylalanine-tRNA ligase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 6.1.1.20 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9055-66-7 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Search | |
|---|---|
| PMC | articles |
| PubMed | articles |
| NCBI | proteins |
| Ferredoxin-fold anticodon binding domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
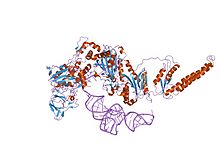
the crystal structure of phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase from Thermus thermophilus complexed with cognate tRNAPhe
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | FDX-ACB | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF03147 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR005121 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1pys | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1pys | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
In enzymology, a phenylalanine-tRNA ligase (EC 6.1.1.20) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The 3 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, L-phenylalanine, and tRNAPhe, whereas its 3 products are AMP, diphosphate, and L-phenylalanyl-tRNAPhe.
This enzyme belongs to the family of ligases, to be specific those forming carbon-oxygen bonds in aminoacyl-tRNA and related compounds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-phenylalanine:tRNAPhe ligase (AMP-forming). Other names in common use include phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase, phenylalanyl-transfer ribonucleate synthetase, phenylalanine-tRNA synthetase, phenylalanyl-transfer RNA synthetase, phenylalanyl-tRNA ligase, phenylalanyl-transfer RNA ligase, L-phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase, and phenylalanine translase. This enzyme participates in phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis and aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis.
Phenylalanine-tRNA synthetase (PheRS) is known to be among the most complex enzymes of the aaRS (Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase) family. Bacterial and PheRSs share a ferredoxin-fold anticodon binding (FDX-ACB) domain, which represents a canonical double split alpha+beta motif having no insertions. The FDX-ACB domain displays a typical RNA recognition fold (RRM) formed by the four-stranded antiparallel beta sheet, with two helices packed against it.
...
Wikipedia
