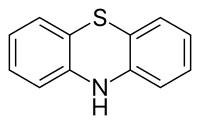
Phenothiazines
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
10H-Phenothiazine
|
|
| Other names
Thiodiphenylamine
Dibenzothiazine Dibenzoparathiazine 10H-dibenzo-[b,e]-1,4-thiazine PTZ |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
92-84-2 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:37931 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL828 |
| ChemSpider |
21106365 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.997 |
| KEGG |
D02601 |
| UNII |
GS9EX7QNU6 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C12H9NS | |
| Molar mass | 199.27 g/mol |
| Appearance | greenish-yellow rhombic leaflets or diamond-shaped plates |
| Melting point | 185 °C (365 °F; 458 K) |
| Boiling point | 371 °C (700 °F; 644 K) |
| 0.00051 g/L (20 °C) | |
| Solubility in other solvents | benzene, ether, petroleum ether, chloroform, hot acetic acid, ethanol (slightly), mineral oil (slightly) |
| Acidity (pKa) | approx 23 in DMSO |
| -114.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
none |
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 5 mg/m3 [skin] |
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D. |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Phenothiazine abbreviated PTZ is an organic compound that has the formula S(C6H4)2NH and is related to the thiazine-class of heterocyclic compounds.
It is used in chemical manufacturing as a stabilizer or inhibitor. It was used in the mid-20th century as an insecticide and antihelminthic for livestock and humans, but was superseded by other compounds.
Derivatives of phenothiazine discovered in the 1940s revolutionized the field of psychiatry and allergy treatment. The earliest derivative, methylene blue, was one of the first antimalarial drugs, and as of 2015 derivatives are under investigation as possible anti-infective drugs. It is a prototypical pharmaceutical lead structure in modern medicinal chemistry.
In the manufacture of monomers, phenothiazine is used as a chemical stabilizer or inhibitor to prolong storage and shelf life of products such as acryloyl chloride.
Phenothiazine was formerly used as an insecticide and as a drug to treat infections with parasitic worms (antihelminthic) in and people, but its use for those purposes has been superseded by other chemicals.
Phenothiazine was introduced by DuPont as an insecticide in 1935. About 3,500,000 pounds were sold in the US in 1944. However, because it was degraded by sunlight and air, it was difficult to determine how much to use in the field, and its use waned in the 1940s with the arrival of new pesticides like DDT that were more durable. As of July 2015 it is not registered for pesticide use in the US, nor Europe, nor Australia.
...
Wikipedia
