Peptide T
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
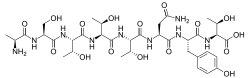
L-Alanyl-L-seryl-L-threonyl-L-threonyl-L-threonyl-L-asparaginyl-L-tyrosyl-L-threonine
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
106362-32-7 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 66081 |
| PubChem | 73352 |
| UNII |
05DYM3ZS1X |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C35H55N9O16 | |
| Molar mass | 857.87 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Peptide T is an HIV entry inhibitor discovered in 1986 by researchers at the National Institutes of Health in the United States. Peptide T, and its modified analog Dala1-peptide T-amide (DAPTA), a drug in clinical trials, is a short peptide derived from the HIV envelope protein gp120 which blocks binding and infection of viral strains which use the CCR5 receptor to infect cells.
Peptide T has several positive effects related to HIV disease and Neuro-AIDS. A FDG-PET neuro-imaging study in an individual with AIDS dementia who completed a 12-wk treatment with intranasal DAPTA, showed remission in 34 out of 35 brain regions after treatment. (PMID 8965193). A placebo-controlled, three site, 200+ patient NIH-funded clinical trial, which focused on neurocognitive improvements, was conducted between 1990 and 1995. The results showed that DAPTA was not significantly different from placebo on the study primary end points. However, 2 of 7 domains, abstract thinking and speed of information processing, did show improvement in the DAPTA group (p<.05). Furthermore, twice as many DAPTA-treated patients improved, whereas twice as many placebo patients deteriorated (P=.02). A sub-group analysis showed that DAPTA had a treatment effect and improved global cognitive performance (P=.02) in the patients who had more severe cognitive impairment.
A long-delayed analysis of antiviral effects from the 1996 NIH study showed peripheral viral load (combined plasma and serum) was significantly reduced in the DAPTA-treated group. An eleven-person study for peptide T effects on cellular viral load showed reductions in the persistently infected monocyte reservoir to undetectable levels in most of the patients. Elimination of viral reservoirs, such as the monocytes, is an important treatment goal. DAPTA has been shown to substantially suppress brain inflammation and block proinflammatory cytokine signaling pathways in a small animal model of Alzheimer's disease.
An orally administered analog of Peptide T/DAPTA prevented neuropathic pain from developing, or reversed it once it had occurred, (animals) by blocking chemokine receptors CCR2 and CCR5, microglial activation, the infiltration of monocytes into spinal cord, and inhibiting the inflammatory cytokines evoked by peripheral nerve injury that causes chronic pain. Peptide T/DAPTA has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions which may underlie the described cognitive benefits and suggests uses in brain injuries and neurodegenerative diseases.(See PMID 22033364, PMID 19034668, PMID 23147416, PMID 24316469).
...
Wikipedia
