Peony
| Peony | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Paeonia suffruticosa | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Core eudicots |
| Order: | Saxifragales |
| Family: |
Paeoniaceae Raf. |
| Genus: |
Paeonia L. |
| sections | |
and for lower taxa see text |
|
 |
|
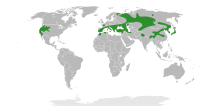
| The range of Paeonia. | |
and for lower taxa see text
The peony or paeony is a flowering plant in the genus Paeonia, the only genus in the family Paeoniaceae. They are native to Asia, Europe and Western North America. Scientists differ on the number of species that can be distinguished ranging from 25 to 40, although the current consensus is 33 known species. The relationships between the species need to be further clarified.
Most are herbaceous perennial plants 0.25–1 metre (0.82–3.28 ft) tall, but some are woody shrubs 0.25–3.5 metres (0.82–11.48 ft) tall. They have compound, deeply lobed leaves and large, often fragrant flowers, in colors ranging from purple red to white or yellow, in late spring and early summer.
Peonies are among the most popular garden plants in temperate regions. Herbaceous peonies are also sold as cut flower on a large scale, although generally only available in late spring and early summer.
All Paeoniaceae are deciduous perennial herbs or shrubs, with thick storage roots and thin roots for gathering water and minerals. Some species are caespitose, because the crown produces adventitous buds, while others have stolons. They have rather large compound leaves without glands and stipules, and with anomocytic stomata. In the woody species the new growth emerges from scaly buds on the previous flush or from the crown of the rootstock. The large bisexual flowers are mostly single at the end of the stem. In P. emodi, P. lactiflora, P. veitchii and many of the cultivars these contributed to, few additional flowers develop in the axils of the leaves. Flowers close at night or when the sky is overcast. Each flower is subtended by a number of bracts, that may form a sort of involucre, has 3-7 tough free sepals and mostly 5-8, but occasionally up to 13 free petals. These categories however are intergrading, making it difficult to assign some of them, and the number of these parts may vary. Within are numerous (50–160) free stamens, with anthers fixed at their base to the filaments, and are sagittate in shape, open with longitudal slits at the outer side and free pollen grains which have three slits or pores and consist of two cells. Within the circle of stamens is a more or less prominent, lobed disc, which is presumed not to excrete nectar. Within the disk is a varying number (1-15) of separate carpels, which have a very short style and a decurrent stigma. Each of these develops into a dry fruit (which is called a follicle), which open with a lengthwise suture and each of which contain one or a few large fleshy seeds. The annual growth is predetermined: if the growing tip of a shoot is removed, no new buds will develop that season.
...
Wikipedia
