Pelvic inflammatory diseases
| Pelvic inflammatory disease | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Pelvic inflammatory disorder |
 |
|
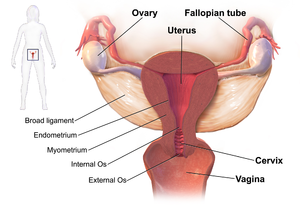
| Drawing showing the usual sites of infection in pelvic inflammatory disease | |
| Specialty | Gynecology |
| Symptoms | Lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever, burning with urination, pain with sex, irregular menstruation |
| Complications | Infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, cancer |
| Causes | Bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix |
| Risk factors | Gonorrhea, chlamydia |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, ultrasound, laparoscopic surgery |
| Prevention | Not having sex, having few sexual partners, using condoms |
| Treatment | Antibiotics |
| Frequency | 1.5 percent of young women yearly |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
Pelvic inflammatory disease or pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID) is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often there may be no symptoms. Signs and symptoms, when present may include lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever, burning with urination, pain with sex, or irregular menstruation. Untreated PID can result in long term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, and cancer.
The disease is caused by bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix. Infections by Neisseria gonorrhoeae or Chlamydia trachomatis are present in 75 to 90 percent of cases. Often multiple different bacteria are involved. Without treatment about 10 percent of those with a chlamydial infection and 40 percent of those with a gonorrhea infection will develop PID. Risk factors are similar to those of sexually transmitted infections generally and include a high number of sexual partners and drug use.Vaginal douching may also increase the risk. The diagnosis is typically based on the presenting signs and symptoms. It is recommended that the disease be considered in all women of childbearing age who have lower abdominal pain. A definitive diagnosis of PID is made by finding pus involving the fallopian tubes during surgery.Ultrasound may also be useful in diagnosis.
...
Wikipedia
