Parathion-ethyl
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
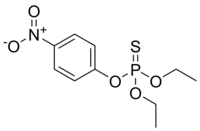
O,O-Diethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate
|
|
| Other names
E605
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
56-38-2 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:27928 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL261919 |
| ChemSpider |
13844817 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.247 |
| KEGG |
C06604 |
| UNII |
61G466064D |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H14NO5PS | |
| Molar mass | 291.26 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals (pure form) |
| Melting point | 6 °C (43 °F; 279 K) |
| 24 mg/L | |
| Solubility in other solvents | high solubility |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | [1] |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|
| R-phrases | R24, R26/28, R48/25, R50/53 |
| S-phrases | S28, S36/37, S45, S60, S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
5 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 10 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 3 mg/kg (dog, oral) 0.93 mg/kg (cat, oral) 5 mg/kg (horse, oral) 8 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 2 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
|
LC50 (median concentration)
|
84 mg/m3 (rat, 4 hr) |
|
LCLo (lowest published)
|
50 mg/m3 (rabbit, 2 hr) 14 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 2 hr) 15 mg/m3 (mouse) |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
none (methyl parathion), TWA 0.1 mg/m3 [skin] (ethyl parathion) |
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.2 mg/m3 [skin] (methyl parathion) TWA 0.05 mg/m3 [skin] (ethyl parathion) |
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D. (methyl parathion) 10 mg/m3 (ethyl parathion) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Parathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion and locally known as "Folidol", is an organophosphate compound possessing a organothiophosphate group. It is a potent insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans. Its use is banned or restricted in many countries, and there are proposals to ban it from all use. The basic structure is shared by parathion methyl.
Parathion was developed by Gerhard Schrader for the German trust IG Farben in the 1940s. After the war and the collapse of IG Farben due to the war crime trials, the Western allies seized the patent, and parathion was marketed worldwide by different companies and under different brand names. The most common German brand was E605 (banned in Germany after 2002); this was not a food-additive "E number" as used in the EU today. "E" stands for Entwicklungsnummer (German for "development number"). It is an irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.
Safety concerns have later lead to the development of parathion methyl, which is somewhat less toxic.
When pure, parathion is a white crystalline solid. It is commonly distributed as a brown liquid that smells of rotting eggs or garlic. The insecticide is somewhat stable, although it darkens when exposed to sunlight.
Parathion is synthesized from diethyl dithiophosphoric acid (C2H5O)2PS2H by chlorination to generate diethylthiophosphoryl chloride ((C2H5O)2P(S)Cl). In a salt metathesis reaction, the chloride treated with sodium 4-nitrophenolate (the sodium salt of 4-nitrophenol).
...
Wikipedia

