Papilledema
| Papilledema | |
|---|---|
 |
|
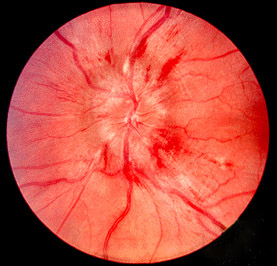
| Fundal photograph showing severe papilloedema in the left eye | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Neurosurgery |
| ICD-10 | H47.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 377.0 |
| DiseasesDB | 9580 |
| eMedicine | oph/187 |
| Patient UK | Papilledema |
| MeSH | D010211 |
Papilledema (or papilloedema) is optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks. Unilateral presentation is extremely rare. Papilledema is mostly seen as a symptom resulting from another pathophysiological process.
In intracranial hypertension, papilledema most commonly occurs bilaterally. When papilledema is found on fundoscopy, further evaluation is warranted as vision loss can result if the underlying condition is not treated. Further evaluation with a CT or MRI of the brain and/or spine is usually performed. Recent research has shown that point-of-care ultrasound can be used to measure optic nerve sheath diameter for detection of increased intracranial pressure and shows good diagnostic test accuracy compared to CT. Thus, if there is a question of papilledema on fundoscopic examination or if the optic disc cannot be adequately visualized, ultrasound can be used to rapidly assess for increased intracranial pressure and help direct further evaluation and intervention. Unilateral papilledema can suggest a disease in the eye itself, such as an optic nerve glioma.
Papilledema may be asymptomatic or present with headache in the early stages. However it may progress to enlargement of the blind spot, blurring of vision, visual obscurations (inability to see in a particular part of the visual field for a period of time) and ultimately total loss of vision may occur.
The signs of papilledema that are seen using an ophthalmoscope include:
On visual field examination, the physician may elicit an enlarged blind spot; the visual acuity may remain relatively intact until papilledema is severe or prolonged.
Checking the eyes for signs of papilledema should be carried out whenever there is a clinical suspicion of raised intracranial pressure, and is recommended in newly onset headaches. This may be done by ophthalmoscopy or fundus photography, and possibly slit lamp examination.
...
Wikipedia
