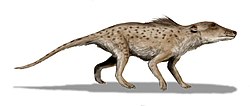
Pakicetidae
| Pakicetidae Temporal range: Early Eocene, 52–48 Ma |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Pakicetus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Infraorder: | Cetacea |
| Parvorder: | †Archaeoceti |
| Family: |
†Pakicetidae Thewissen, Madar & Hussain 1996 |
| Genera | |
Pakicetus
Nalacetus
Ichthyolestes
Pakicetidae ("Pakistani whales") is an extinct family of early whales that lived during the Early Eocene on the shores of Pakistan.
Dehm & Oettingen-Spielberg 1958 described the first pakicetid, Ichthyolestes, but at the time they did not recognize it as a cetacean, but identified it as a fish-eating mesonychid. Robert West was the first to identify pakicetids as cetaceans in 1980 and, after discovering a braincase, Phillip Gingerich and Donald Russell described the genus Pakicetus in 1981. During the following two decades, more research resulted in additional pakicetid cranial material and by 2001 postcranial material for the family had been described. Though all parts of pakicetid postcrania are known, no complete skeleton from a single individual has been recovered. The pakicetid goldmine is the "H-GSP Locality 62" site in the Kala Chitta Hills where fossils from all three genera have been found. However, this site is so littered with bones that identifying bones from a single individual is impossible, and pakicetid skeletons are consequently composites of bones from several individuals.
Pakicetids have been found in or near river deposits in northern Pakistan and northwestern India, a region which was probably arid with only temporary streams when these animals lived there. No pakicetids have been found in marine deposits, and they were apparently terrestrial or freshwater animals. Their long limbs and small hands and feet also indicate they were poor swimmers. Their bones are heavy and compact and were probably used as ballast; they clearly indicate pakicetids were not fast runners notwithstanding their otherwise cursorial morphology. Most likely, pakicetids lived in or near bodies of freshwater and their diet can have included both land animals and aquatic organisms.
Pakicetid ears had an external auditory meatus and ear ossicles (i.e. incus, malleus, tympanic ring, etcetera) similar to those in living land mammals and most likely used normal land mammal hearing in air. In the pakicetid mandible, the mandibular foramen is small and comparable in size to those of extant land mammals and the acoustic mandibular fat pad characteristic of later whales was obviously not present. The lateral wall of the mandible is also relatively thick in pakicetids, further preventing sound transmission through the jaw. The tympanic bulla in pakicetid ears is similar to those in all cetaceans, with a relatively thin lateral wall and thickened medial part known as the involucrum. However, in contrast to later cetaceans, the tympanic bone makes contact with the periotic bone which is firmly attached to the skull leaving no space for isolating air sinuses, effectively preventing directional hearing in water. Pakicetids most likely used bone conduction for hearing in water.
...
Wikipedia
