New South Wales state election, 1953
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
All 94 seats in the New South Wales Legislative Assembly 48 Assembly seats were needed for a majority |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
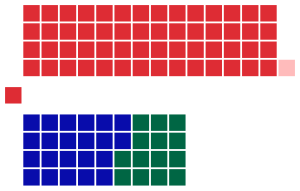
Legislative Assembly after the election
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1953 New South Wales state election was held on 14 February 1953. It was conducted in single member constituencies with compulsory preferential voting and was held on boundaries created at a 1952 redistribution. The election was for all of the 94 seats in the Legislative Assembly.
In February 1953, Labor had been in power for 12 years and James McGirr, who had led the party to a near defeat in 1950, had lost the premiership to Joe Cahill 10 months earlier. McGirr's period as the Labor leader had been marked by policy indecisiveness, budget overspending and internal conflict. Cahill had won popular support as a vigorous and impressive minister who had resolved problems with New South Wales' electricity supply and in his first 10 months as premier had reinvigorated the party. He appeared decisive and brought order to the government's chaotic public works program. In addition, he astutely attacked the increasingly unpopular federal Coalition government of Robert Menzies. In contrast, the Liberal Party and Country Party coalition led by Vernon Treatt and Michael Bruxner was racked with internal divisions and Treatt, despite having been opposition leader for 7 years had been unable to present a coherent alternative to the government or find a resonance with the public. .
The result of the election was a landslide victory for Labor:
Labor's vote was particularly strong in the Western and Southern suburbs of Sydney. It won the seats of Concord, Coogee, Drummoyne, Kogarah, Parramatta, Ryde and Sutherland from the Liberal Party and picked up the new suburban seats of East Hills and Fairfield . Labor's vote was resurgent in rural New South Wales where it won the seats of Armidale, Dubbo and Mudgee from the Country party. Labor also picked up the seat of North Sydney from Independent member James Geraghty who was the last of the 4 Independent members of parliament who had been expelled from the Labor party for disloyalty during an indirect election of the Legislative Council in 1949. John Seiffert, another rebel from 1949 and the member for Monaro, had been readmitted to the party in 1950 and retained the seat at this election, giving a further boost to Labor's numbers. Labor's losses included Ashfield which had been won from the Liberal Party at the 1952 by-election and Hartley which was retained by Jim Chalmers who stood as an Independent Labor candidate after he resigned from the party over a pre-selection dispute. The Minister for Labour, Industry and Social Welfare, Frank Finnan was unseated when his electorate of Darlinghurst was abolished and he failed in an attempt to win Albury. Arthur Greenup also retired when his seat of Newtown-Annandale was abolished.
...
Wikipedia

