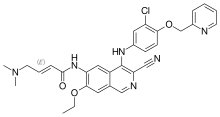
Neratinib
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H29ClN6O3 |
| Molar mass | 557.04 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Neratinib (HKI-272) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor anticancer drug candidate.
Like lapatinib and afatinib, it is a dual inhibitor of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinases. It inhibits them by covalently binding with a cysteine side chain in those proteins.
Neratinib has an IC50 of 59 nM against HER2 and shows weak inhibition against KDR and Scr with IC50 values of 0.8 µM and 1.4 µM, respectively. In BT474 cells, neratinib reduces HER2 autophosphorylation, and inhibited cyclin D1 expression while reduced proliferation has been observed A431 cells when treated with neratinib at concentrations of 3 or 5 nM. In xenograft models with 3T3/neu tumors oral administration of neratinib at 10, 20, 40 or 80 mg/kg was able to inhibit tumor growth while in SK-OV-3 models doses of 5 and 60 mg/kg significantly inhibited tumor growth.
Neratinib was discovered and initially developed by Wyeth; Pfizer continued development up to Phase III in breast cancer, and sold it to Puma Biotechnology in 2011.
In September 2016 Puma submitted a new drug application to the US FDA for neratinib as a treatment for some people with HER-2 positive breast cancer.
In July 2017 it was approved by the US FDA for adjuvant treatment of adult patients with early stage HER2-overexpressed/amplified breast cancer, (after adjuvant trastuzumab-based therapy).
...
Wikipedia
