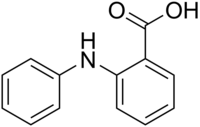
N-Phenylanthranilic acid
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
2-(phenylamino)benzoic acid
|
|
| Other names
N-phenylanthranilic acid
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.879 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C13H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 213.23 g/mol |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Fenamic acid is a molecule which, especially in its ester form, fenamate, serves as a parent structure for several nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including mefenamic acid, tolfenamic acid, flufenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid. These drugs are commonly referred to as "anthranilic acid derivatives" or "fenamates" because fenamic acid is a derivative of anthranilic acid.
...
Wikipedia
