Muscarine
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
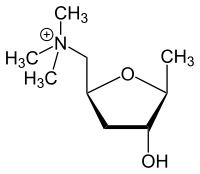
2,5-Anhydro-1,4,6-trideoxy-6-(trimethylammonio)-D-ribo-hexitol
|
|
| Other names
L-(+)-muscarine, muscarin, (2S,4R,5S)-(4-hydroxy-5-methyl-tetrahydrofuran-2-ylmethyl)-trimethyl-ammonium
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
300-54-9 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL12587 |
| ChemSpider |
8949 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.541 |
| 3996 | |
| PubChem | 9308 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C9H20NO2+ | |
| Molar mass | 174.26 g/mol |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Muscarine, L-(+)-muscarine, or muscarin is a natural product found in certain mushrooms, particularly in Inocybe and species, such as the deadly . Mushrooms in the genera Entoloma and Mycena have also been found to contain levels of muscarine which can be dangerous if ingested. Muscarine has been found in harmless trace amounts in Boletus, Hygrocybe, Lactarius and Russula. Muscarine is only a trace compound in the fly agaric Amanita muscaria; the pharmacologically more relevant compound from this mushroom is muscimol. A. muscaria fruitbodies contain a variable dose of muscarine, usually around 0.0003% fresh weight. This is very low and toxicity symptoms occur very rarely. Inocybe and Clitocybe contain muscarine concentrations up to 1.6%.
Muscarine is a nonselective agonist of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor.
Muscarine was first isolated from Amanita muscaria by German chemists Oswald Schmiedeberg and Richard Koppe, who reported their findings in 1869. It was the first parasympathomimetic substance ever studied and causes profound activation of the peripheral parasympathetic nervous system that may end in convulsions and death. Being a quaternary ammonium salt, muscarine is less completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract than tertiary amines, but it does not cross the blood-brain barrier. Muscarinic agonists activate muscarinic receptors while nicotinic agonists activate nicotine receptors. Both are direct-acting cholinomimetics; they produce their effects by binding to and activating cholinergic receptors. Final proof of the structure was given by Franz Jellinek and colleagues in 1957 with the help of X-ray diffraction analysis; Jellinek further described the three-dimensional structure of the molecule using muscarine chloride. These new findings set into motion research not only on the pharmacology of muscarine, but also on that of muscarine-like substances that are structurally related to acetylcholine.
...
Wikipedia
