Mountain goats
| Mountain goat | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Caprinae |
| Genus: | Oreamnos |
| Species: | O. americanus |
| Binomial name | |
|
Oreamnos americanus (Blainville, 1816) |
|
 |
|
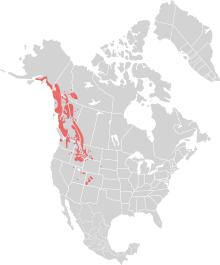
The mountain goat (Oreamnos americanus), also known as the Rocky Mountain goat, is a large hoofed mammal endemic to North America. A subalpine to alpine species, it is a sure-footed climber commonly seen on cliffs and ice.
Despite its vernacular name, it is not a member of Capra, the genus that includes all other goats, such as the wild goat, Capra aegagrus, from which the domestic goat is derived.
The mountain goat is an even-toed ungulate of the order Artiodactyla and the family Bovidae that includes antelopes, gazelles, and cattle. It belongs to the subfamily Caprinae (goat-antelopes), along with 32 other species including true goats, sheep, the chamois, and the muskox. The mountain goat is the only species in the genus Oreamnos. The name Oreamnos is derived from the Greek term oros (stem ore-) "mountain" (or, alternatively, oreas "mountain nymph") and the word amnos "lamb".
Both billy (male) and nanny (female) mountain goats have beards, short tails, and long black horns, 15–28 cm (5.9–11.0 in) in length, which contain yearly growth rings. They are protected from the elements by their woolly white double coats. The fine, dense wool of their undercoats is covered by an outer layer of longer, hollow hairs. Mountain goats molt in spring by rubbing against rocks and trees, with the adult billies shedding their extra wool first and the pregnant nannies shedding last. Their coats help them to withstand winter temperatures as low as −50 °F (−46 °C) and winds of up to 100 mph (160 km/h).
...
Wikipedia

