Mount Ślęża
| Ślęża | |
|---|---|

View from north-west
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 718 m (2,356 ft) |
| Coordinates | 50°51′54.061″N 16°42′31.741″E / 50.86501694°N 16.70881694°E |
| Geography | |
| Location | Poland, Lower Silesian Voivodeship |
| Parent range | Ślęża Massif |
| Topo map | 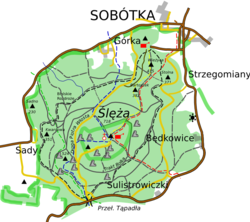 |
The Ślęża [ˈɕlɛ̃ʐa] (German: Zobten or Zobtenberg, later also Siling) is a mountain in the Sudeten Foreland (Polish: Przedgórze Sudeckie) in Lower Silesia, 30 km (19 mi) from Wrocław, southern Poland. This natural reserve built mostly of granite is 718 m high and covered with forests.
The top of the mountain has a PTTK tourist Mountain hut, a TV and radio mast, church Mary, poorly visible ruins of the castle and observation tower. The mountain and its surrounding region form the protected area called Ślęża Landscape Park.
During the Neolithic Period and at least as far back as the 7th century BC Mount Ślęża (Zobten) was a holy place of the tribes of the Lusatian culture. It was then settled by Celts and later by Germanic Lugians. Scientists believe that the sacred wood of the Alcis from Germanic mythology mentioned by Tacitus in his Germania was located on Mount Ślęża. The Silingi, a subpopulation of the East Germanic tribe known as the Vandals are the earliest inhabitants of Silesia known by their name, however the greater part of them moved westwards after the 5th century A.D. and the remainder were slowly replaced in the 6th century by Slavic tribes who assimilated the few remaining East Germanic inhabitants. The Silingi were part of the Przeworsk culture. The name of the territory Silesia either derives from the Ślęza River, or from Mount Ślęża, which themselves derive their name from either, according to Germanist authors the Silingi people. or, according to Slavisist authors, the Ślężanie people.
...
Wikipedia
