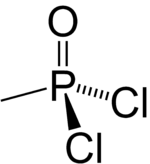
Methylphosphonic acid dichloride
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Methylphosphonic dichloride
|
|
| Other names
Methanephosphonic dichloride
Methanephosphonic acid dichloride Methylphosphonyl dichloride |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.578 |
| EC Number | 211-634-4 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| CH3Cl2OP | |
| Molar mass | 132.91 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.468 g/mL at 20 °C |
| Melting point | 28 to 34 °C (82 to 93 °F; 301 to 307 K) |
| Boiling point | 163 °C (325 °F; 436 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Very Toxic |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R14, R23/24/25, R26, R34 |
| Flash point | >110 °C |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
26 ppm/4h by inhalation (rat) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Methyl phosphonic dichloride is an organophosphorus compound. It has a number of potential uses but is most notable as being a precursor to several chemical weapons agents. It is a white crystalline solid, with a low melting point. It hydrolyzes readily and must be handled with care as it is exceedingly toxic.
Methyl phosphonic dichloride is produced by oxidation of methyldichlorophosphine, e.g. with sulfuryl chloride:
It can also be produced from a range of methyl-phosphonates (e.g. dimethyl methylphosphonate) via chlorination with thionyl chloride. Various amines can be used to catalyse this process. It reacts with hydrogen fluoride or sodium fluoride to produce methylphosphonyl difluoride, which is used in the production of sarin and soman nerve agents.
...
Wikipedia
