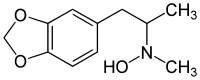
Methylenedioxyhydroxymethamphetamine
 |
|
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15NO3 |
| Molar mass | 209.24 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-hydroxy-N-methylamphetamine (MDHMA; FLEA) is an entactogen, psychedelic, and stimulant of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It is the N-hydroxy homologue of MDMA ("Ecstasy"), and the N-methyl homologue of MDOH. MDHMA was first synthesized and assayed by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved), Shulgin listed the dosage range as 100–160 mg, and the duration as approximately 4–8 hours. He describes MDHMA as causing entactogenic and open MDMA-like effects, easing communication, and increasing appreciation of the senses.
...
Wikipedia
