Metabolic syndrome
| Dysmetabolic syndrome X | |
|---|---|
 |
|
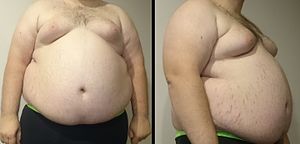
| A morbidly obese man. Weight 182 kg/400 lbs, height 185 cm/6 ft 1 in. The body mass index is 53. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
| ICD-10 | E88.9 |
| ICD-9-CM | 277.7 |
| OMIM | 605552 |
| DiseasesDB | 31955 |
| MedlinePlus | 007290 |
| Patient UK | Metabolic syndrome |
| MeSH | D024821 |
Metabolic syndrome, sometimes known by other names, is a clustering of at least three of the five following medical conditions (giving a total of 16 possible combinations giving the syndrome):
Metabolic syndrome is associated with the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Some studies have shown the prevalence in the USA to be an estimated 34% of the adult population, and the prevalence increases with age.
Insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and prediabetes are closely related to one another and have overlapping aspects.
The syndrome is thought to be caused by an underlying disorder of energy utilization and storage. The cause of the syndrome is an area of ongoing medical research.
The main sign of metabolic syndrome is central obesity (also known as visceral, male-pattern or apple-shaped adiposity), overweight with adipose tissue accumulation particularly around the waist and trunk.
Other signs of metabolic syndrome include high blood pressure, decreased fasting serum HDL cholesterol, elevated fasting serum triglyceride level (VLDL triglyceride), impaired fasting glucose, insulin resistance, or prediabetes.
Associated conditions include hyperuricemia, fatty liver (especially in concurrent obesity) progressing to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, polycystic ovarian syndrome (in women), erectile dysfunction (in men), and acanthosis nigricans.
...
Wikipedia
