Meropenem
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Merrem |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% |
| Protein binding | Approximately 2% |
| Biological half-life | 1 hour |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.170.691 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
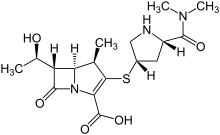
| Formula | C17H25N3O5S |
| Molar mass | 383.464 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Meropenem is an ultra-broad-spectrum antibiotic used to treat a wide variety of infections. It is a β-lactam and belongs to the subgroup of carbapenems, similar to imipenem and ertapenem.
Meropenem was developed by Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma and patented in 1983. It gained US FDA approval in July 1996. It penetrates well into many tissues and body fluids, including cerebrospinal fluid, bile, heart valve, lung, and peritoneal fluid. It was initially marketed by AstraZeneca under the trade name Merrem.
The spectrum of action includes many Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (including Pseudomonas) and anaerobic bacteria. The overall spectrum is similar to that of imipenem, although meropenem is more active against Enterobacteriaceae and less active against Gram-positive bacteria. It works against extended-spectrum β-lactamases, but may be more susceptible to metallo-β-lactamases. Meropenem is frequently given in the treatment of febrile neutropenia. This condition frequently occurs in patients with hematological malignancies and cancer patients receiving anticancer drugs that suppress bone marrow formation. It is approved for complicated skin and skin structure infections, complicated intra-abdominal infections and bacterial meningitis.
...
Wikipedia
