Ertapenem
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Invanz |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Intramuscular, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% (intramuscular) |
| Protein binding | Inversely proportional to concentration; 85 to 95% |
| Metabolism | Minor hydrolysis of beta-lactam ring, not involved |
| Biological half-life | 4 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (80%) and fecal (10%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
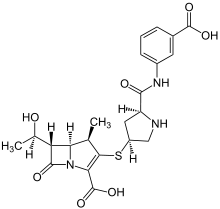
| Formula | C22H25N3O7S |
| Molar mass | 475.516 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ertapenem is a carbapenem antibiotic marketed by Merck as Invanz. It is structurally very similar to meropenem in that it possesses a 1-β-methyl group. Other members of the carbapenem group (imipenem, doripenem, and meropenem) are broadly active antibacterials that are used for infections caused by difficult to treat or multidrug-resistant bacteria (such as ESBL expressing Klebsiella pneumonia). They have very short serum half-lives and must be administered by intravenous infusion every 6 to 8 hours. Ertapenem differs from other carbapenems in having a somewhat less broad spectrum of activity (not against Pseudomonas aeruginosa), and in that its extended serum half-life allows it to be administered once every 24 hours.
Ertapenem has been designed to be effective against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. It is not active against MRSA, ampicillin-resistant enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, or Acinetobacter species. Ertapenem also has clinically useful activity against anaerobic bacteria.
Ertapenem has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following micro-organisms in vitro and in clinical infections.
Aerobic and facultative gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates only), Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible isolates only), Streptococcus pyogenes,
Note: Methicillin-resistant staphylococci and Enterococcus spp. are resistant to ertapenem.
...
Wikipedia
