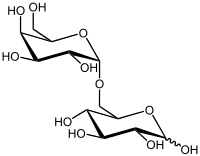
Melibiose
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-6-[[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
5340-95-4 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:28053 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL1159652 |
| ChemSpider |
10974 |
| MeSH | Melibiose |
| PubChem | 11458 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C12H22O11 | |
| Molar mass | 342.30 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 84-85 °C |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Melibiose is a reducing disaccharide formed by an alpha-1,6 linkage between galactose and glucose (D-Gal-α(1→6)-D-Glc). It differs from lactose in the chirality of the carbon where the galactose ring is closed and that the galactose is linked to a different point on the glucose moiety. It can be formed by invertase-mediated hydrolysis of raffinose, which produces melibiose and fructose. Melibiose can be broken down into its component saccharides, glucose and galactose, by the enzyme Alpha-galactosidase, such as MEL1 from Saccharomyces pastorianus (lager yeast).
Melibiose cannot be used by Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ale yeast), this is one test to differentiate between the two yeast species.
...
Wikipedia
