Madagascar succulent woodlands
| Madagascar succulent woodlands | |
|---|---|

|
|
 |
|
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Afrotropic |
| Biome | Deserts and xeric shrublands |
| Borders | Madagascar dry deciduous forests, Madagascar subhumid forests, Madagascar spiny forests |
| Animals | Standing's day gecko, flat-backed spider tortoise |
| Bird species | Appert's greenbul |
| Mammal species | Malagasy giant rat, Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, Verreaux's sifaka, narrow-striped mongoose |
| Geography | |
| Area | 79,700 km2 (30,800 sq mi) |
| Country | Madagascar |
| Elevation | 0–600 metres (0–1,969 ft) |
| Coordinates | 22°36′S 44°36′E / 22.600°S 44.600°ECoordinates: 22°36′S 44°36′E / 22.600°S 44.600°E |
| Geology | Sands, sandstone, limestone, metamorphic, and igneous basement rocks |
| Climate type | Hot semi-arid climate (BSh) |
| Soil types | Sandy |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | Critical, endangered |
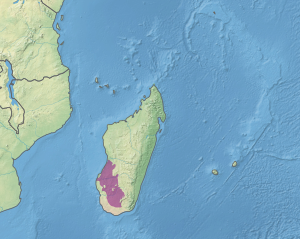
The Madagascar succulent woodlands are a xeric shrublands ecoregion in southwestern and central western Madagascar. They are threatened by various human activities.
The succulent woodlands are found in the southwest and centre-west of Madagascar, in the rain shadow region that receives less moisture than the east and the Central Highlands. The climate is tropical and dry, with rainfall ranging from 575 to 1,330 mm per year, and a marked dry season from May to October.
To the north, the succulent woodlands make a transition into the Madagascar dry deciduous forests, while to the south, they border the even drier Madagascar spiny thickets and to the east, the Madagascar subhumid forests.
The vegetation is similar to the dry deciduous forests to the north, but includes more dry-adapted, xerophytic species. Forests, reaching 15 metres (49 ft) in height, contain trees and shrubs of the families Burseraceae, Euphorbiaceae, Fabaceae, and Sapindaceae. Notable endemics include two species of baobab, Adansonia za and A. grandidieri (near threatened and endangered, respectively), and succulents in the genus Pachypodium.
Between 60 and 90 bird species and eight lemur species are found in the ecoregion and a number of mammals, frogs, and reptiles are endemic to the area. A notable lemur species is the endangered Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, the world's smallest primate.
...
Wikipedia
