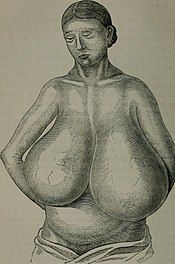
Macromastia
| Breast hypertrophy | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Gynecology, endocrinology |
| ICD-10 | N62 |
| ICD-9-CM | 611.1 |
| DiseasesDB | 1628 |
Breast hypertrophy is a rare medical condition of the breast connective tissues in which the breasts become excessively large. The condition is often divided based on the severity into two types, macromastia and gigantomastia. Hypertrophy of the breast tissues may be caused by increased histologic sensitivity to certain hormones such as female sex hormones, prolactin, and growth factors. Breast hypertrophy is a benign progressive enlargement, which can occur in both breasts (bilateral) or only in one breast (unilateral). It was first scientifically described in 1648.
The indication is a breast weight that exceeds approximately 3% of the total body weight. There are varying definitions of what is considered to be excessive breast tissue, that is the expected breast tissue plus extraordinary breast tissue, ranging from as little as 0.6 kilograms (1.3 lb) up to 2.5 kilograms (5.5 lb) with most physicians defining macromastia as excessive tissue of over 1.5 kilograms (3.3 lb). Some resources distinguish between macromastia (Greek, macro: large, mastos: breast), where excessive tissue is less than 2.5 kg, and gigantomastia (Greek, gigantikos: giant), where excessive tissue is more than 2.5 kg. The enlargement can cause muscular discomfort and over-stretching of the skin envelope, which can lead in some cases to ulceration.
Hypertrophy of the breast can affect the breasts equally, but usually affects one breast more than the other, thereby causing asymmetry, when one breast is larger than the other. The condition can also individually affect the nipples and areola instead of or in addition to the entire breast. The effect can produce a minor size variation to an extremely large breast asymmetry. Breast hypertrophy is classified in one of five ways: as either pubertal (virginal hypertrophy), gestational (gravid macromastia), in adult women without any obvious cause, associated with penicillamine therapy, and associated with extreme obesity. Many definitions of macromastia and gigantomastia are based on the term of "excessive breast tissue", and are therefore somewhat arbitrary.
...
Wikipedia
