Lognormal
Log-normal
|
Probability density function
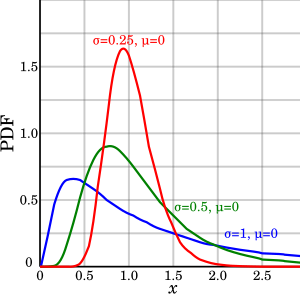
Some log-normal density functions with identical location parameter  but differing scale parameters but differing scale parameters 
|
|
Cumulative distribution function

Cumulative distribution function of the log-normal distribution (with  ) )
|
| Notation |
 |
| Parameters |
 — location, — location,
 — scale — scale
|
| Support |
 |
| PDF |
 |
| CDF |
![{\frac {1}{2}}+{\frac {1}{2}}\,\mathrm {erf} {\Big [}{\frac {\ln x-\mu }{{\sqrt {2}}\sigma }}{\Big ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3cde9b1ecbbb13897c36b45898ebbd7cd2366ecc) |
| Mean |
 |
| Median |
 |
| Mode |
 |
| Variance |
![{\displaystyle [\exp({\sigma ^{2}}\!\!)-1]*\exp({2\mu +\sigma ^{2}})}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e283edefb1b3afc7e344a84d6a4d4edd51c20cd9) |
| Skewness |
 |
| Ex. kurtosis |
 |
| Entropy |
 |
| MGF |
defined only for numbers with a non-positive real part, see text |
| CF |
representation  is asymptotically divergent but sufficient for numerical purposes is asymptotically divergent but sufficient for numerical purposes |
| Fisher information |
 |
In probability theory, a log-normal (or lognormal) distribution is a continuous probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is normally distributed. Thus, if the random variable  is log-normally distributed, then
is log-normally distributed, then  has a normal distribution. Likewise, if
has a normal distribution. Likewise, if  has a normal distribution, then the exponential function of
has a normal distribution, then the exponential function of  is
is  has a log-normal distribution. A random variable which is log-normally distributed takes only positive real values. The distribution is occasionally referred to as the Galton distribution or Galton's distribution, after Francis Galton. The log-normal distribution also has been associated with other names, such as McAlister, Gibrat and Cobb–Douglas.
has a log-normal distribution. A random variable which is log-normally distributed takes only positive real values. The distribution is occasionally referred to as the Galton distribution or Galton's distribution, after Francis Galton. The log-normal distribution also has been associated with other names, such as McAlister, Gibrat and Cobb–Douglas.
...
Wikipedia











![{\frac {1}{2}}+{\frac {1}{2}}\,\mathrm {erf} {\Big [}{\frac {\ln x-\mu }{{\sqrt {2}}\sigma }}{\Big ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3cde9b1ecbbb13897c36b45898ebbd7cd2366ecc)



![{\displaystyle [\exp({\sigma ^{2}}\!\!)-1]*\exp({2\mu +\sigma ^{2}})}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e283edefb1b3afc7e344a84d6a4d4edd51c20cd9)








