Lithium cobalt oxide
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
lithium cobalt(III) oxide
|
|
| Other names
lithium cobaltite
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
12190-79-3 |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.135 |
| PubChem | 23670860 |
| Properties | |
| LiCoO 2 |
|
| Molar mass | 97.87 g mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | harmful |
| R-phrases | R42/43 |
| S-phrases | S36 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO
2) is a chemical compound commonly used in the positive electrodes of lithium-ion batteries. The structure of LiCoO
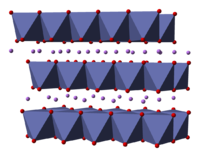
2 has been studied with numerous techniques including x-ray diffraction, electron microscopy, neutron powder diffraction, and EXAFS: it consists of layers of lithium that lie between slabs of octahedra formed by cobalt and oxygen atoms. The space group is in Hermann-Mauguin notation, signifying a rhombus-like unit cell with threefold improper rotational symmetry and a mirror plane. More simply, however, both lithium and cobalt are octahedrally coordinated by oxygen. These octahedra are edge-sharing, and tilted relative to the layered structure. The threefold rotational axis (which is normal to the layers) is termed improper because the triangles of oxygen (being on opposite sides of each octahedron) are anti-aligned.
...
Wikipedia

