Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide
 Monomer (does not exist)
|
|
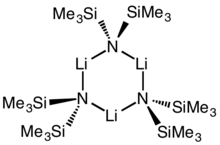 Cyclic trimer
|
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Lithium 1,1,1-trimethyl-N-(trimethylsilyl)silanaminide
|
|
| Other names
Lithium hexamethyldisilazide
Hexamethyldisilazane lithium salt |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.569 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H18LiNSi2 | |
| Molar mass | 167.326 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 0.86 g/cm3 at 25 °C |
| Melting point | 71 to 72 °C (160 to 162 °F; 344 to 345 K) |
| Boiling point | 80 to 84 °C (176 to 183 °F; 353 to 357 K) (0.001 mm Hg) |
| decomposes | |
| Solubility | Most aprotic solvents THF, hexane, toluene |
| Acidity (pKa) | 26 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | flammable, corrosive |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide Potassium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide is a lithiated organosilicon compound with the formula LiN(SiMe3)2. It is commonly abbreviated as LiHMDS (lithium hexamethyldisilamide - a reference to its conjugate acid HMDS) and is primarily used as a strong non-nucleophilic base and as a ligand. Like many lithium reagents it has a tendency to aggregate and will form a cyclic trimer in the absence of coordinating species.
LiHMDS is commercially available, but it can also be prepared by the deprotonation of bis(trimethylsilyl)amine with n-butyllithium. This reaction can be performed in situ.
Once formed, the compound can be purified by sublimation or distillation.
LiHMDS is often used in organic chemistry as a strong non-nucleophilic base. Its conjugate acid has a pKa of ~26 making it is less basic that other lithium bases, such as LDA (pKa of conjugate acid ~36), but it is more sterically hindered and hence less nucleophilic. It can be used to form various organolithium compounds including acetylides, or lithium enolates.
As such it finds use in a range of coupling reactions; particularly carbon-carbon bond forming reactions such as the Fráter–Seebach alkylation and mixed Claisen condensations.
...
Wikipedia
