Non-nucleophilic base
As the name suggests, a non-nucleophilic base is an organic base that is a poor nucleophile. Normal bases are also nucleophiles, but often chemists seek the proton-removing ability of a base without any other functions. Typical non-nucleophilic bases are bulky, such that protons can attach to the basic center but alkylation and complexation is inhibited.
A variety of amines and nitrogen heterocycles are useful bases of moderate strength (pKa of conjugate acid around 10-13)
Non-nucleophilic bases of high strength are usually anions. For these species the pKa's of the conjugate acid is around 35-40.
Other strong non-nucleophilic bases are sodium hydride and potassium hydride. These compounds are dense, salt-like materials that are insoluble and operate by surface reactions.
Some reagents are of high basicity (pKa of conjugate acid around 17) but of modest but not negligible nucleophilicity. Examples include sodium tert-butoxide and potassium tert-butoxide.
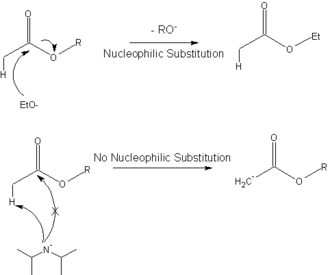
The following diagram shows how the hindered base, lithium diisopropylamide, is used to deprotonate an ester to give the enolate in the Claisen ester condensation, instead of undergoing a nucleophilic substitution.
This reaction (deprotonation with LDA) is commonly used to generate enolates.
...
Wikipedia