Leucovorin
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Leucovorin /luːkoʊˈvɔːrɪn/ |
| Trade names | Many |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
intravenous, IM, by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Dose dependent |
| Protein binding | ~15% |
| Biological half-life | 6.2 hours |
| Excretion | Urinary |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | citrovorum factor, 5-formyltetrahydrofolate |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.621 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
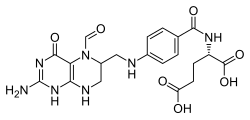
| Formula | C20H23N7O7 |
| Molar mass | 473.44 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Melting point | 245 °C (473 °F) decomp |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Folinic acid, also known as leucovorin, is a medication used to decrease the toxic effects of methotrexate and pyrimethamine. It is also used in combination with 5-fluorouracil to treat colorectal cancer, may be used to treat folate deficiency that results in anemia, and methanol poisoning. It is taken by mouth, injection into a muscle, or injection into a vein.
Side effects may include trouble sleeping, allergic reactions, or fever. Use in pregnancy or breastfeeding is generally regarded as safe. When used for anemia it is recommended that pernicious anemia as a cause be ruled out first. Folinic acid is a form of folic acid that does not require activation by dihydrofolate reductase to be useful to the body.
Folinic acid was first made in 1945. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. In the United Kingdom it costs the NHS about 4.62 pounds per 30 mg vial.
Folinic acid is administered at the appropriate time following methotrexate as part of a total chemotherapeutic plan, where it may "rescue" bone marrow and gastrointestinal mucosa cells from methotrexate. No apparent effect is seen on pre-existing methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity. Folinic acid can be taken as a pill (orally) or injected into a vein (intravenously) or muscle (intramuscularly).
...
Wikipedia
