Johnston Atoll
|
Johnston Atoll Kalama Atoll (Hawaiian) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| United States Minor Outlying Islands | |||
|
|||
| Anthem: "The Star-Spangled Banner" | |||
 Map of Johnston Atoll |
|||
| Location in the Pacific Ocean | |||
| Coordinates: 16°44′13″N 169°31′26″W / 16.73694°N 169.52389°WCoordinates: 16°44′13″N 169°31′26″W / 16.73694°N 169.52389°W | |||
| Country | United States | ||
| Status | unorganized, unincorporated territory | ||
| Claimed by U.S. | March 19, 1858 | ||
| Named for | Captain Charles J. Johnston, HMS Cornwallis | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | administered as a National Wildlife Refuge | ||
| • Body | United States Fish and Wildlife Service | ||
| • Superintendent | Susan White, Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 1.03 sq mi (2.67 km2) | ||
| • EEZ | 157,389 sq mi (407,635 km2) | ||
| Highest elevation (Sand Island) | 30 ft (10 m) | ||
| Lowest elevation (Pacific Ocean) | 0 ft (0 m) | ||
| Time zone | Hawaii–Aleutian Time Zone (UTC-10) | ||
| Geocode | 127 | ||
| ISO 3166 code | UM | ||
| Currency | US dollar (USD) | ||
| Website | www |
||
Johnston Atoll, also known as Kalama Atoll to Native Hawaiians, is an unincorporated territory of the United States currently administered by the United States Air Force (USAF) of the United States Department of Defense. The islands are visited annually by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Public entry is only by special-use permit from the United States Air Force.
For nearly 70 years, the atoll was under the control of the American military. In that time it was used as a bird sanctuary, as a naval refueling depot, as an airbase, for nuclear and biological weapons testing, for space recovery, as a secret missile base, and as a chemical weapon and Agent Orange storage and disposal site. These activities left the area environmentally contaminated and remediation and monitoring continue.
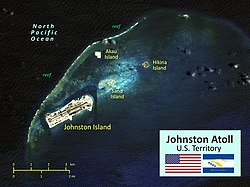
The Johnston Atoll is a deserted 1,300 ha (3,200 acres) atoll in the North Pacific Ocean located about 750 nmi (860 mi; 1,390 km) southwest of the island of Hawai'i and is grouped as one of the United States Minor Outlying Islands. The atoll, which is located on a coral reef platform, has four islands. Johnston (or Kalama) Island and Sand Island are both enlarged natural features, while Akau (North) and Hikina (East) are two artificial islands formed by coral dredging. By 1964, dredge and fill operations had increased the size of Johnston Island to 596 acres (241 ha) from its original 46 acres (19 ha), also increased Sand Island from 10 to 22 acres (4.0 to 8.9 ha), and added two new islands, North and East, of 25 and 18 acres (10.1 and 7.3 ha).
The four islands compose a total land area of 2.67 square kilometres (1.03 square miles). Due to the atoll's tilt, much of the reef on the southeast portion has subsided. But even though it does not have an encircling reef crest, the reef crest on the northwest portion of the atoll does provide for a shallow lagoon, with depths ranging from 3–10 m (9.8–32.8 ft). The climate is tropical but generally dry. Northeast trade winds are consistent and there is little seasonal temperature variation. With elevation ranging from sea level to 5 m (16 ft) at Summit Peak, the islands contain some low-growing vegetation and palm trees on mostly flat terrain and no natural fresh water resources.
...
Wikipedia