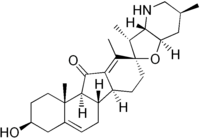
Jervine
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(2'R,3S,3'R,3'aS,6'S,6aS,6bS,7'aR,11aS,11bR)-2,3,3'a,4,4',5',6,6',6a,6b,7,7',7'a,8,11a,11b- Hexadecahydro-3-hydroxy-3',6',10,11b-tetramethyl-spiro[9H-benzo[a]fluorene- 9,2'(3'H)-furo[3,2-b] pyridin]-11(1H)-one
|
|
| Other names
(3β,23β)-17,23-Epoxy-3-hydroxyveratraman-11-one
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.745 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C27H39NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 425.60 g/mol |
| Solubility | 10 mg/mL in EtOH 6 mg/mL in DMF |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Jervine is a steroidal alkaloid with molecular formula C27H39NO3 which is derived from the Veratrum plant genus. Similar to cyclopamine, which also occurs in the Veratrum genus, it is a teratogen implicated in birth defects when consumed by animals during a certain period of their gestation.
Jervine is a potent teratogen causing birth defects in vertebrates. In severe cases it can cause cyclopia and holoprosencephaly.
Jervine's biological activity is mediated via its interaction with the 7 pass trans membrane protein smoothened. Jervine binds with and inhibits smoothened, which is an integral part of the hedgehog signaling pathways. With smoothened inhibited, the GLI1 transcription cannot be activated and hedgehog target genes cannot be transcribed.
...
Wikipedia
