Isuprel
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Many |
| MedlinePlus | a601236 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Inhalation (80–120 μg) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Biological half-life | ~2 minutes |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | isoproterenol (USAN) |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.807 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
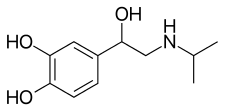
| Formula | C11H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 211.258 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Isoprenaline (isoproterenol) is a medication used for the treatment of bradycardia (slow heart rate), heart block, and rarely for asthma. In humans, it is a non-selective β adrenoreceptor agonist that is the isopropylamine analog of epinephrine (adrenaline).
It is used to treat heart block and episodes of Adams-Stokes syndrome that are not caused by ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, in emergencies for cardiac arrest until electric shock can be administered, for bronchospasm occurring during anesthesia, and as an adjunct in the treatment of hypovolemic shock, septic shock, low cardiac output (hypoperfusion) states, congestive heart failure, and cardiogenic shock.
Historically, it was used to treat asthma via metered aerosol or nebulizing devices; it was also available in sublingual, oral, intravenous, and intramuscular formulations. The U.S. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Expert Panel recommends against its use as a nebulizer for acute bronchoconstriction; the use of any beta2-agonists including isoprenaline is not recommended in an asthmatic respiration crisis.
It should not be used in people with tachyarrhythmias, tachycardia or heart block caused by digitalis poisoning, ventricular arrhythmias which require inotropic therapy, or with angina.
Adverse effects of isoprenaline include nervousness, headache, dizziness, nausea, visual blurring, tachycardia, palpitations, angina, Adams-Stokes attacks, pulmonary edema, hypertension, hypotension, ventricular arrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias, difficulty breathing, sweating, mild tremors, weakness, flushing, and pallor.
Isoprenaline is a β1 and β2 adrenoreceptor agonist and has almost no activity against alpha adrenergic receptors. Its agonist effects at TAAR1 provide it with a pharmacodynamic effects that resemble those of the endogenous trace amines, like tyramine.
...
Wikipedia
